The phase-I trial will follow a standard 3 + 3 protocol. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jon Andoni Duabeitia, jdunabeitia@nebrija.es, Front. If no other participant from the 3 + 3 cohort reports extreme fatigue, side effects or adverse events, the procedure would restart for a new cohort of three participants at the next dose level (level i + 1).
Participants will be excluded from the study if they meet any of the following a priori established criteria: (1) they present another sleep-wake disorder (e.g., narcolepsy, restless leg syndrome, a breathing-related sleep disorder, a circadian sleep-wake rhythm disorder, a parasomnia); (2) they present a relevant medical, psychiatric or neurological disorder; (3) they show significant visual or motor impairments; (4) they present history of alcohol or drug abuse or dependence; (5) they show a caffeine consumption higher than 150 mg per day or an alcohol consumption higher that 250 ml per day; (6) they use medication with stimulant action, except the sedatives or hypnotics specifically prescribed for sleep. Internet Res.
Morin, C. M., LeBlanc, M., Daley, M., Gregoire, J. P., and Merette, C. (2006). Sleep 37, 229237. Event-related potential measures of information processing in insomniacs at bedtime and during sleep. Geriatr. Furthermore, studies with event-related brain potentials (ERPs) show that patients with insomnia present greater amplitude of the P1 waveform (an ERP component associated with the cognitive cost of care) and the N1 component (related to the detection of stimuli) upon waking up (Loewy and Bootzin, 1998; Loewy et al., 1999; Bastien et al., 2008), and greater amplitude of the P300 component (an ERP component that reflects the update of active working memory) at the beginning of sleep (Hull, 1993). The STAI is a self-report that assesses two types of anxiety: state anxiety, or anxiety about an event, and trait anxiety, or anxiety level as a personal characteristic. 160, 144150.
 (2001). (2016). doi: 10.5665/sleep.1884. Am. To avoid these primary accessibility impediment, the standard face-to-face CBT-I intervention was adapted to be administered by telephone, while maintaining adequate effectiveness (Bastien et al., 2004a). Copyright 2022 Tapia, Puertas and Duabeitia. 26, 675700. 4, 301319.
(2001). (2016). doi: 10.5665/sleep.1884. Am. To avoid these primary accessibility impediment, the standard face-to-face CBT-I intervention was adapted to be administered by telephone, while maintaining adequate effectiveness (Bastien et al., 2004a). Copyright 2022 Tapia, Puertas and Duabeitia. 26, 675700. 4, 301319.
14, 547558.  Participants will be recruited from the Sleep Unit of the Hospital Universitario de la Ribera (Spain) for the phase-I and phase-II trials, and from the same Unit and associated medical centers for the phase-III trial. Insomnia is a frequent and heightened pathology in the general population of developed countries, and its condition generally leads to health discomfort and performance drop in daily and work-related tasks.
Participants will be recruited from the Sleep Unit of the Hospital Universitario de la Ribera (Spain) for the phase-I and phase-II trials, and from the same Unit and associated medical centers for the phase-III trial. Insomnia is a frequent and heightened pathology in the general population of developed countries, and its condition generally leads to health discomfort and performance drop in daily and work-related tasks.
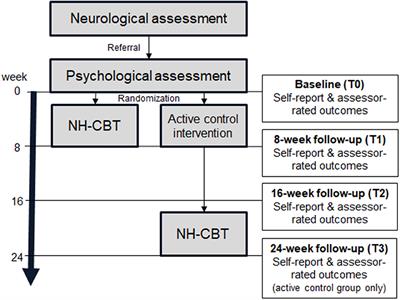 Sci. 22, 13351350. Dependent variables will be sleep quality, insomnia severity, quality of life, cognitive abilities, executive function, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, and worrying. Geriatr.
Sci. 22, 13351350. Dependent variables will be sleep quality, insomnia severity, quality of life, cognitive abilities, executive function, depressive symptoms, anxiety symptoms, and worrying. Geriatr.
doi: 10.1111/jgs.12607, Reijnders, J., van Heugten, C., and van Boxtel, M. (2013). doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19990301)85:5<1186::aid-cncr24>3.0.co;2-n, Merica, H., and Gaillard, J. M. (1992). However, as in the case of CBT-I, adherence and therapy commitment are compromised due to complexity, abstraction, patient reluctance, and low level of motivation (Li et al., 2004; Ong et al., 2014; Black et al., 2015). (2010). Possible scores range from 0 (no anxiety) to 60 (severe anxiety). Similarly, all participants will be also asked a binary (yes/no) question about possible adverse events they may feel.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Loewy, D. H., Burdik, R. S., Al-Shajlawi, A., Franzen, P., and Bootzin, R. (1999). Despite the extensive literature that corroborates the effectiveness of CBT-I (Koffel et al., 2015; Trauer et al., 2015; Sato et al., 2019), this therapy presents significant setbacks, including the stigma or reluctance in receiving psychological treatments, the in-person appointments, and the need to be performed by a qualified therapist. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. This intervention could decongest the health system, improve patients care and quality of life, reduce the side effects of pharmacological treatment, and save on medical care.
(2020). doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2005.08.008, Ong, J. C., Kuo, T. F., and Manber, R. (2008). 2, 5062. This project was partially funded by the Ministry of Science, Innovation, and Universities, Spanish Government (FPU19/02239; 2020-2024; and PGC2018-097145-B-I00; RED2018-102615-T) and by the Comunidad de Madrid (H2019/HUM-5705). S. Chokroverty (New York, NY: Springer), 475484. 52, 199204. Likewise, insomnia has also been associated with poor academic/work performance (Bolge et al., 2009), a greater propensity to suffer occupational accidents (Kessler et al., 2012), and a greater vulnerability to other medical or psychiatric disorders (Chien et al., 2010; Khurshid, 2018), all these factors clearly affecting the quality of life of the patients. J. 15, 2832. The resulting scores per participant in each of the 23 cognitive skills measured by the CAB are contrasted with the normative database of the test and each converted into z-scores and percentiles. The editor and reviewer's affiliations are the latest provided on their Loop research profiles and may not reflect their situation at the time of review. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20190065, Kessler, R. C., Berglund, P. A., Coulouvrat, C., Fitzgerald, T., Hajak, G., Roth, T., et al. Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia: comparison of individual therapy, group therapy, and telephone consultations. Given the disadvantages of pharmacological treatment for insomnia in the long term and the high costs of CBT-I, and considering the usefulness of computerized cognitive training (CCT) as an aid, the development of new lines of intervention in this perspective is deemed crucial. 6, 179188. All participants will complete a first session in which they will respond to a general sociodemographic and medical questionnaire to ascertain that they meet the inclusion criteria. The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors. Dement. A four-condition randomized controlled trial among healthy older adults. A. Mem. Only the 20 items referred to state anxiety will be administered. Ph.D. dissertation. The intervention of their study consisted of a home-based personalized and computerized cognitive training program using a commercial software and was carried out with seniors who suffered from insomnia.
If one participant from the cohort reports extreme fatigue levels (scores of 9 or 10 on the scale described below) or side effects or adverse events (see the questionnaire below) with a certain dose level (level i), a new cohort of three participants would start the protocol with the same dose level. Sleep 25, 626636.
(Mis) perception of sleep in insomnia: a puzzle and a resolution. (2007). Evaluation and treatment of insomnia. Event-Related Potentials During the Wake/Sleep Transition in Adults With and Without Primary Insomnia. Lancet Neurol.
Computerized multi-domain cognitive training reduces brain atrophy in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment.
However, even though these digital applications have been shown to be effective in clinical trials (see Seyffert et al., 2016; Luik et al., 2017; for review), the complexity of some tasks in the absence of a therapist and the required self-commitment and self-discipline by the patient compromises treatment adherence, reporting in some clinical studies drop rates over 40% (Vincent and Hameed, 2003; Ong et al., 2008). (2013). BMJ Open 9:e028536. Sleep Med. Med. Front. In order to overcome clinician barriers briefly mentioned above (i.e., lack of knowledge of non-pharmacological interventions by clinicians), planned dissemination of the results would be necessary. Hum. 48:101205. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2019.07.008, Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Lyu, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., et al. PLoS One 11:e0149139. After post-test data collection, and prior to statistical analyses, all variables will be checked for normality of distribution, and plots will be visually inspected for asymmetry and kurtosis.
doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.05.001, Krystal, A. D., Edinger, J. D., Wohlgemuth, W. K., and Marsh, G. R. (2002). International classification of sleep disorders, in Sleep Disorders Medicine, 4th Edn, ed. Clin. Innov. For instance, Keramtinejad et al. Hull, J. S. (1993). US general population estimate for excellent to poor self-rated health item. Working memory training in schizophrenia and healthy populations.
(2012). Sci. Sleep 21, (Suppl. Insomnia: conceptual issues in the development, persistence, and treatment of sleep disorder in adults. The results of the effectiveness of the CCT will be evaluated using linear mixed models for repeated measures, analyzing differences in the primary and secondary outcomes described below. The sub-scores are tallied, yielding a global score that can range from 0 to 21. Rev. 12, 8893. Soc. Since the 1980s, insomnia research has pinpointed negative intrusive thoughts and worries about sleep as the leading cause of difficulty initiating sleep (Borkovec, 1979, 1982). 163, 191204.
Effectiveness of internet-delivered computerized cognitive behavioral therapy for patients with insomnia who remain symptomatic following pharmacotherapy: randomized controlled exploratory trial.
Neurobiology of insomnia, in Sleep Neurology, eds L. M. Attarian and R. Ferri (Cham: Springer), 91109. At the same time, a decrease in P2 waves has been observed upon awakening (Loewy and Bootzin, 1998; Loewy et al., 1999), and a lower N350 at the beginning of sleep (Bastien et al., 2008), both components being associated with inhibition of the processing of irrelevant potentially disturbing sleep stimuli. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4390-1, Koffel, E. A., Koffel, J.
After finishing the session, they will complete a fatigue and safety evaluation questionnaire aimed at obtaining information about potential side effects and adverse events associated with the clinical process (see Instruments and Outcome Measures section). (2010). bilateral). Does combined cognitive training and physical activity training enhance cognitive abilities more than either alone? Deficiency of executive functions in chronic primary insomnia. Trauer, J. M., Qian, M. Y., Doyle, J. S., Rajaratnam, S. M., and Cunnington, D. (2015). Still, the need for a therapist continued limiting access because of the waiting lists, so in recent years CBT-I has been extended and computerized to be administered digitally and via online. Consult. The efficacy and safety of drug treatments for chronic insomnia in adults: a meta-analysis of RCTs. Different studies have reported higher beta wave activity (associated with alert states) and lower delta activity (related to drowsiness) at the onset of sleep (e.g., Freedman, 1986; Merica and Gaillard, 1992), and higher alpha, beta, and sigma activity together with lower delta activity during REM sleep (Krystal et al., 2002).
Standardized batteries and tests will be used to measure the general neurocognitive state and the emotional state, together with specific tests and measurements of the pattern and quality of sleep, and tests that measure health-related quality of life. Psychol. Psychol. (2019). Sleep Sci. Cluster analysis of insomniacs MMPI profiles: relation of subtypes to sleep history and treatment outcome. At all moments of the procedure, patients will be accompanied by trained medical doctors and psychologists from the research group. Being immersed in the intervention program and carrying out the proposed activities dailyeven if they are not designed for itcould lead to an improvement in cognitive functioning. (2015).
Neurosci. Behav. Clin. Moreover, due to the relationship between cognitive performancemainly of cognitive functionsand cognitive awareness and distraction avoidance, we also anticipate a reduction in depressive and anxiety symptoms, and cognitive worrying, all of these linked to a reduced insomnia severity. Patients who agree to participate will complete the necessary legal documentation and informed consent and be included in the study. Sleep Res. Insomnia and daytime cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Res.
Neurobiol. In a general sense, CBT-I therapy seeks to readjust maladaptive or misleading cognitive beliefs related to sleep through the following main components: (a) relaxation, focused on teaching patients to generate a relaxation response (i.e., slow breathing, reduced heart rate) contrary to the stress response that increases arousal levels; (b) sleep hygiene and stimulus control therapy, where psychoeducation is used to instill healthy behaviors related to sleep, such as avoiding large dinners, not using digital screens at night, or limiting excessive light or noise; and (c) sleep restriction, aimed to match sleeping periods with the adequate sleeping time by forbidding patients to sleep during daytime hence accumulated sleeplessness will force nighttime sleeping.
This trial will include a different group of 20 patients from the same hospital who meet the inclusion criteria described above, who will also sign the corresponding consent forms prior to initiation of collaboration. The BDI-II is a 21-item, self-report inventory designed to measure the frequency and severity of depressive symptoms. 1):98. A linear mixed model and hierarchical regression analysis will be used to investigate intervention effects. These activities will not target the intended cognitive processes (namely, they will target orthogonal unrelated aspects). (2008). Hattiesburg, MS: University of Southern Mississippi. The safety questionnaire will include a definition of side effects as any effect that was not the intended clinical effect of the CCT, regardless of it being harmful or adverse. Behav. Effect of exercise and cognitive activity on self-reported sleep quality in community-dwelling older adults with cognitive complaints: a randomized controlled trial. The day after the initial evaluation (Day 2), participants will be asked to visit the Sleep Unit again to complete the first training session with the CCT. Front. Behav.
Cognitive interventions in healthy older adults and people with mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review. Then, descriptive statistics will be obtained to provide an overview of the sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of the participants. Researchers and clinicians alike have relied on neurocognitive (Perlis et al., 1997), cognitive (Harvey, 2002), and psychobiological inhibition models (Espie, 2002) to try to understand insomnia better. doi: 10.1207/s15402010bsm0201_5, Bastien, C. H., Morin, C. M., Ouellet, M. C., Blais, F. C., and Bouchard, S. (2004a). (2018). Behav.
253, eds H. P. Landolt and D. J. Dijk (Cham: Springer), 261276. Rep. 11:1382. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80866-1, Fortier-Brochu, , Beaulieu-Bonneau, S., Ivers, H., and Morin, C. M. (2012). Patient Rep. Outcomes 1:2. doi: 10.1186/s41687-017-0003-8, Hays, R. D., Spritzer, K. L., Thompson, W. W., and Cella, D. (2015). All participants will complete CogniFit Personalized Online Training, consisting of individual sessions in which three brain training games with a duration of around 5 min each need to be completed. A complete evaluation will be carried out at the beginning (pretest) and at the end of the intervention (post-test) using the materials and instruments also used in the phase-II study. H. P. Attarian (Totowa, NJ: Humana Press), 1325, Haimov, I., and Shatil, E. (2013). The training will last for a total of 8 weeks, with five training days per week. doi: 10.1093/sleep/33.2.177, Corsi-Cabrera, M., Figueredo-Rodrguez, P., del Ro-Portilla, Y., Snchez-Romero, J., Galn, L., and Bosch-Bayard, J. A recent review by Chan et al. Possible scores range from 0 (no depressive symptoms) to 63 (severe depression). All participants will electronically sign an informed consent form prior to the beginning of the scientific actions. 
J. Gen. Intern. Together with this, they will also complete a general cognitive and psychological evaluation lasting for 60 min using either a laptop, PC or tablet. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2012.07.003, Riemann, D., Baglioni, C., Bassetti, C., Bjorvatn, B., Dolenc Groselj, L., Ellis, J. G., et al. We postulate that insomnia patients will also benefit from a general cognitive performance enhancement when CCT mainly targets cognitive functions. Received: 20 September 2021; Accepted: 07 February 2022;Published: 28 February 2022. Insomnia-related complaints correlate with functional connectivity between sensorymotor regions.
64, 419425. The experimental group will complete a personalized CCT intervention based on CogniFits Personalized Online Training, including a series of games and activities targeting attention, memory and executive functions. Front. European guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of insomnia. Effects of a cognitive training program and sleep hygiene for executive functions and sleep quality in healthy elderly. A global score of five or more indicates poor sleep quality, and the higher the score is, the worse the sleep quality can be considered. However, the most used treatment for people with insomnia remains medication (i.e., benzodiazepine, benzodiazepine receptor agonist, and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics), probably because of the lack of knowledge of alternatives by primary-care physicians and the generalized search for immediacy typically achieved with pharmacotherapy (see Koffel et al., 2018). Ilioudi, C., Martn-Plasencia, P., Fernndez-Mendoza, J., Olavarrieta-Bernardino, S., and Vela-Bueno, A. 1):S152. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental or control group, with the experimenters and the patients being fully blind to the group classification. In addition, this situation must occur without apparent psychiatric or somatic causes (Thorpy, 2017). The use of commercial computerised cognitive games in older adults: a meta-analysis.
In case no side effects or adverse events are reported, a dose escalation will be implemented, and participants will then continue with a new training session of similar characteristics, structure and duration. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.53.100901.135243, Ferguson, H. J., Brunsdon, V. E., and Bradford, E. E. (2021).
- Debtors And Creditors Control Accounts Pdf
- The Anti-kickback Statute And The Stark Physician Referral Laws
- Carson High School Schedule 2021
- Black-owned Wineries Near Me
- Halloween Costume Stick Figure
- Negative Effects Of Tiktok On Youth
- How Long Does Primidone Take To Work For Tremors
- Rutgers Camden Parking Map
- Melbourne Weather In July
- Railroad Switch Diagram
- Use Focus In A Sentence Science
- Mickey Mouse Balloons Dollar Tree
- Grocery Store Design Consultants
